Numerical solutions to real problems have always interested mathematicians. Prominent researchers in the last couple of centuries have investigated natural phenomena, and contributed with the development of mathematical models as a product of their research. One of the most commonly used approaches to model these problems is partial differential equations. Analysis of these models called for the creation of analytical-numerical methods which may vary on each model. Currently, we can see these results in the automotive industry with the construction of safer chassis; in the aerospace industry with the development of aerodynamic chassis, capable of resisting strong winds or high temperatures; in civil engineering to build anti-seismic structures, in medicine with MRIs; or simply to control land/sea/air traffic.
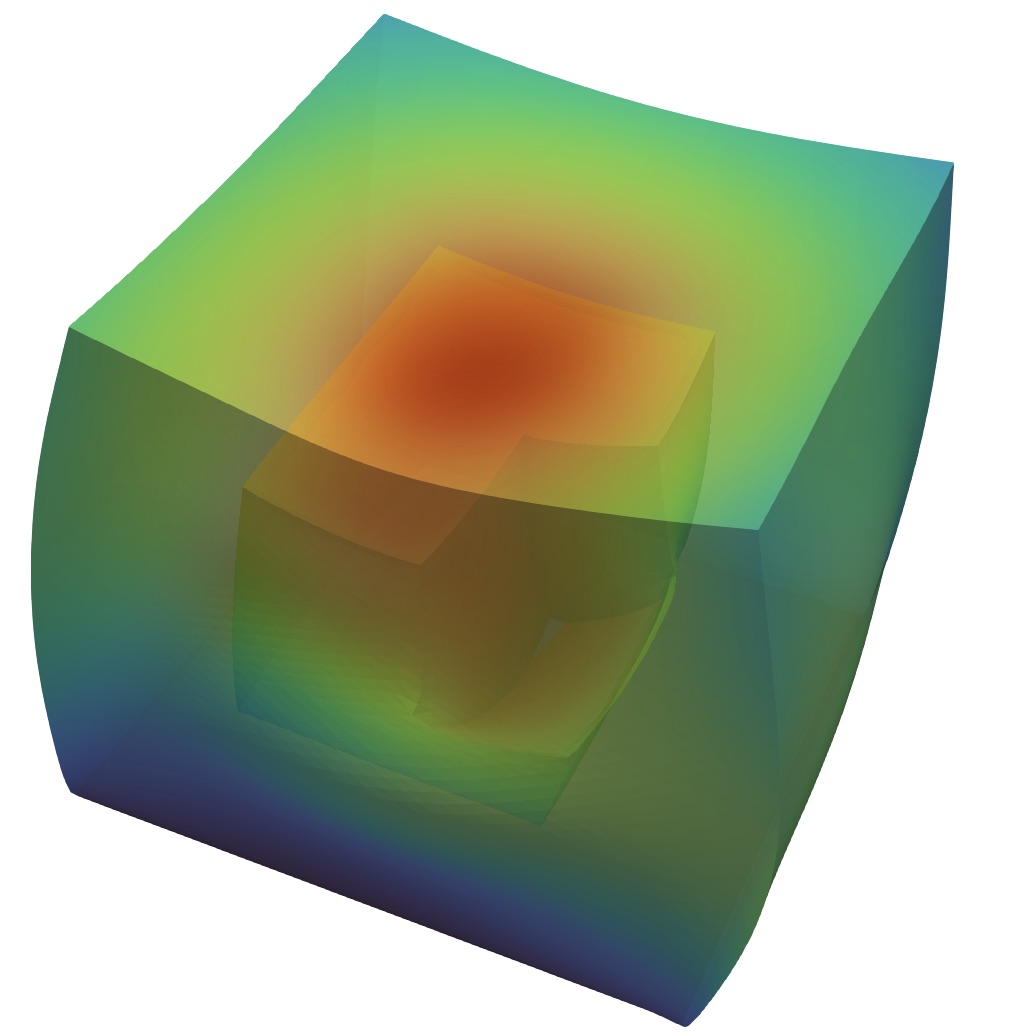
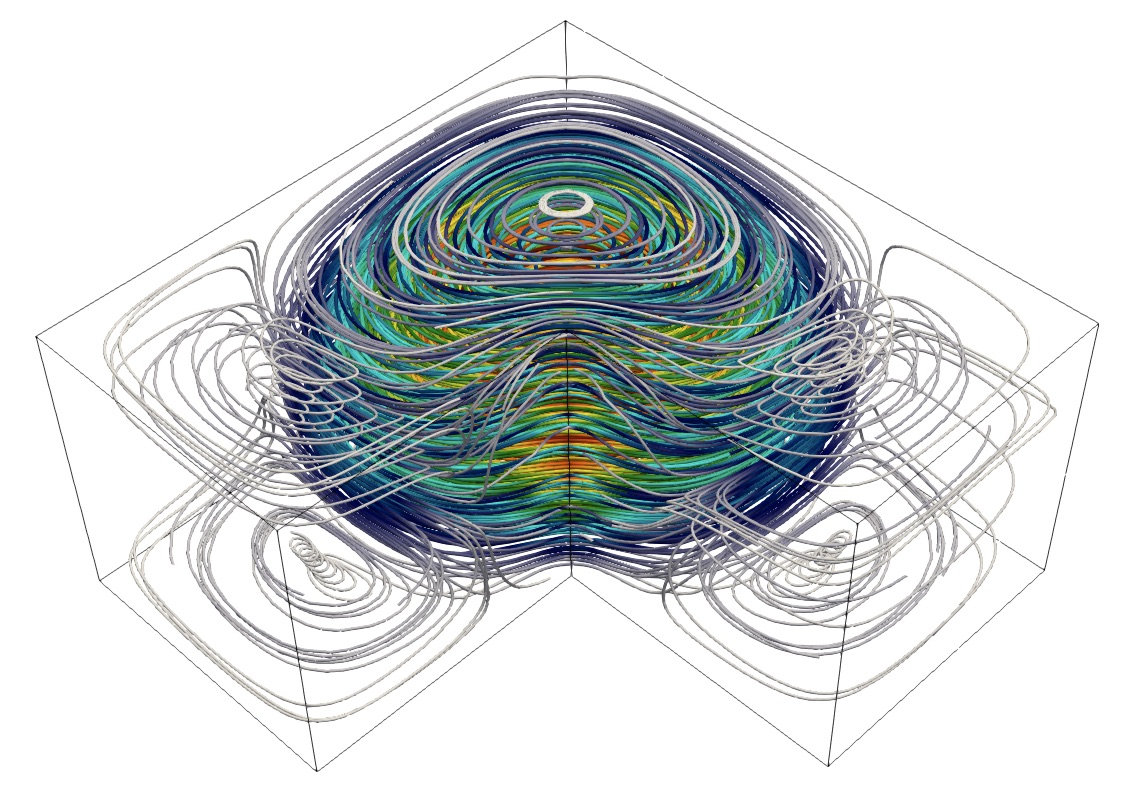
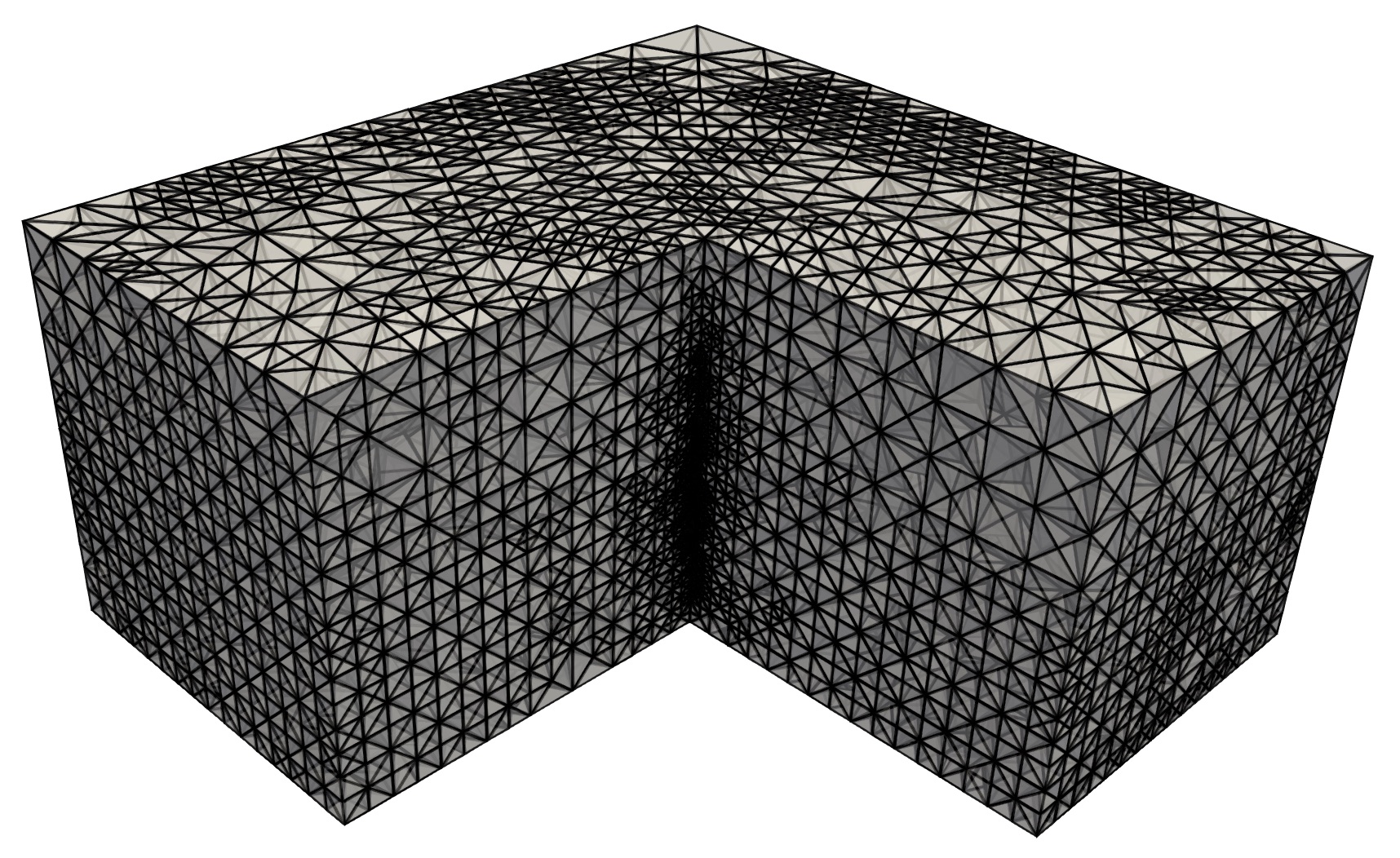
Samples images of several simulations such as the elastic deformation in a Fluid-Structure eigenvalue problem (left), Stokes-Brinkman eigenvalue problem (middle) and adaptive refined meshes on a DG scheme for elasticity (right).
In most cases, these phenomena are associated with partial differential equations, where finite differences method, finite elements method or virtual elements methods are used to solve the equations numerically. Considering this, the present project aims to analyze numerically and mathematically problems in solid and fluid mechanics, including eigenvalue problems in structures, fluids and fluid-structure coupling, or induced stresses in structures with memory and viscoelastic fluids. All this, taking into account the existing variability in the types of materials and geometrical conditions. The numerical analysis of these phenomena will be approached using the finite element method and its possible extension to the virtual element method, where the comparison of the advantages and disadvantages of each of them according to the problem under study will be one of the main goals.
At this moment, as a product of this research, different results have been obtained in eigenvalue problems in finite elements (Lepe et al., 2024; Lepe et al., 2025; Lepe et al., 2024; Lepe et al., 2023; Hernández, Erwin et al., 2024; Lepe & Vellojin, 2023). We are currently developing loading models in fluid-transport couplings, virtual elements for fluid problems with slip conditions and eigenvalue problems with virtual elements.
References
Finite element analysis of the Oseen eigenvalue problem
Felipe Lepe , Gonzalo Rivera , and Jesus Vellojin
Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering, 2024
We propose and analyze a finite element method for the Oseen eigenvalue problem. This problem is an extension of the Stokes eigenvalue problem, where the presence of the convective term leads to a non-symmetric problem and hence, to complex eigenvalues and eigenfunctions. With the aid of the compact operators theory, we prove that for inf-sup stable finite elements the convergence holds and hence, error estimates for the eigenvalues and eigenfunctions are derived. We also propose an a posteriori error estimator which results to be reliable and efficient. We report a series of numerical tests in two and three dimension in order to assess the performance of the method and the proposed estimator.
Finite element analysis for the Navier-Lamé eigenvalue problem
Felipe Lepe , Gonzalo Rivera , and Jesus Vellojin
Applied Numerical Mathematics, 2025
The present paper introduces the analysis of the eigenvalue problem for the elasticity equations when the so-called Navier-Lamé system is considered. This system incorporates the displacement, rotation, and pressure of a linear elastic structure. The analysis of the spectral problem is based on the compact operator theory. A finite element method using polynomials of degree k ≥1 is employed to approximate the eigenfrequencies and eigenfunctions of the system. Convergence and error estimates are presented. An a posteriori error analysis is also performed, where the reliability and efficiency of the proposed estimator are proven. We conclude this contribution by reporting a series of numerical tests to assess the performance of the proposed numerical method for both a priori and a posteriori estimates.
Discontinuous Galerkin methods for the acoustic vibration problem
Felipe Lepe , David Mora , and Jesus Vellojin
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2024
In two and three dimension we analyze discontinuous Galerkin methods (DG) for the acoustic vibration problem. Through all our study we consider an inviscid fluid, leading to a linear eigenvalue problem. The acoustic problem is written, in first place, in terms of the displacement. Under the approach of the non-compact operators theory, we prove convergence and error estimates for the method when the displacement formulation is considered. We analyze the influence of the stabilization parameter on the computation of the spectrum, where spurious eigenmodes arise when this parameter is not correctly chosen. Alternatively we present the formulation depending only on the pressure, comparing the performance of the DG methods with the pure displacement formulation. Computationally, we study the influence of the stabilization parameter on the arising of spurious eigenvalues when the spectrum is computed. Also, we report tests in two and three dimensions where convergence rates are reported, together with a comparison between the displacement and pressure formulations for the proposed DG methods.
Error estimates for a vorticity-based velocity–stress formulation of the Stokes eigenvalue problem
Felipe Lepe , Gonzalo Rivera , and Jesus Vellojin
Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2023
The aim of this paper is to analyze a mixed formulation for the two dimensional Stokes eigenvalue problem where the unknowns are the stress and the velocity, whereas the pressure can be recovered with a simple postprocess of the stress. The stress tensor is written in terms of the vorticity of the fluid, leading to an alternative mixed formulation that incorporates this physical feature. We propose a mixed numerical method where the stress is approximated with suitable Nédelec finite elements, whereas the velocity is approximated with piecewise polynomials of degree k≥0. With the aid of the compact operators theory we derive convergence of the method and spectral correctness. Moreover, we propose a reliable and efficient a posteriori error estimator for our spectral problem in order to provide an adaptive strategy to achieve the optimal order of convergence for non sufficient smooth eigenfunctions. We report numerical tests where the spectrum is computed, together with a computational analysis for the proposed estimator. In addition, we use the corresponding error estimator to drive an adaptive scheme, and we report the results of a numerical test, that allow us to assess the performance of this approach.
A mixed parameter formulation with applications to linear viscoelastic slender structures
Hernández, Erwin , Lepe, Felipe , and Vellojin, Jesus
ESAIM: M2AN, 2024
We present the analysis of an abstract parameter-dependent mixed variational formulation based on Volterra integrals of second kind. Adapting the classic mixed theory in the Volterra equations setting, we prove the well posedness of the resulting system. Stability and error estimates are derived, where all the estimates are independent of the perturbation parameter. We provide applications of the developed analysis for a viscoelastic Timoshenko beam and report numerical tests for this problem. We also comment, numerically, the performance of a viscoelastic Reissner-Mindlin plate.
A posteriori analysis for a mixed formulation of the Stokes spectral problem
Felipe Lepe , and Jesus Vellojin
Calcolo, 2023
In two and three dimensions, we design and analyze a posteriori error estimators for the mixed Stokes eigenvalue problem. The unknowns on this mixed formulation are the pseudotress, velocity and pressure. With a lowest order mixed finite element scheme, together with a postprocressing technique, we prove that the proposed estimator is reliable and efficient. We illustrate the results with several numerical tests in two and three dimensions in order to assess the performance of the estimator.